Linux Systems
How to Setup Android Development Environment With React Native on Ubuntu 16.04
Getting started with android development using react-native.
Warning : This article may contain outdated/inacurate information. Please refer to latest documentation.
In this guide, we won’t install android studio since we will use standard text editor such as atom, sublime text or even gedit. There’s no need to install full blown IDE to develop android with react-native. Since all the necessacy tool and process will be using command line. That’s why we want to install minimal amount of tool to save more storage space. Not only that, we won’t install android virtual device (avd) to save more space and use actual device as testing and debug device.
Note : it is recommended to use actual device instead of virtual device.
Step 1 — Installing Java Development Kit (JDK)
We’ll need java in order to compile source code to apk file. To install java, open your terminal and run following command :
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdkThis will install all the necessary package to start developing java application, in this case android application.
There’s no particular reason why we use openjdk-8, if you need to use older/newer version or other java sdk feel free to install those.
Step 2 — Installing NodeJS and NPM
We need to install nodejs and npm in order to use react-native since react is nodejs module. We will install stable version from ppa maintained by NodeSource (not from ubuntu repository).
For the most recent LST (branch 6.x)
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | sudo -E bash -This will adding PPA into our repository list. Now we need to update package list and installing nodejs into our system.
To verify that nodejs and npm is successfully installed, run the following command.
This will output something like
Step 3 — Install and Setup Android SDK (Command Line Tools only)
Create a new folder in your home directory named Android
Download and extract Android sdk file into Android directory
Go to this page to download command line tools or we can use this link as of 2017-03-17.
Add android sdk into system PATH
Now, we have to add android sdk into our PATH so we can use these command from anywhere. Open file .bashrc from our home directory with text editor. We can use nano or vim to edit this file right from terminal.
Now, add the following line to the end of file to add android sdk into PATH.
We need to restart terminal application for these to take effect.
Installing the right sdk version
React Native require android version 6 (Marshmallow) ro run, so we need to install sdk tool version 23. After restarting terminal application, we’ll install the necessary sdk tool.
Run this command to open android sdk manager.
This will open a new window. From here we can select what package to be installed.
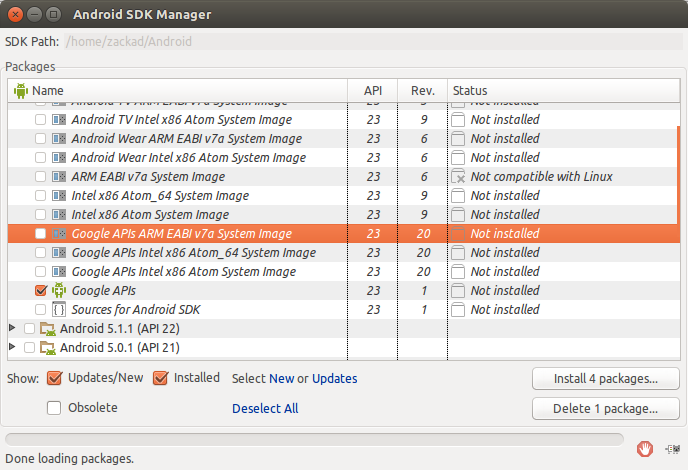
Please make sure that following tool is checked before we click Install Package
Tools/Android SKD Tools Rev.25.xx (265 MB)
Tools/Android SKD Platform-tools Rev.25.xx (7.3 MB)
Tools/Android SDK Build-tools Rev 23.0.1 (37.3 MB)
Android 6.0 (API 23)/SDK Platform (67.2 MB)
Android 6.0 (API 23)/Google APIs (176 KB)
Extras/Android Support Repository (322.7 MB)
Step 4 — Installing React Native
Now, we can install react native command line tool with npm. It is recommended to install this tool globally, so you may need superuser permission. From the terminal, run this command to install react-native-cli.
To verify that react-native successfully installed, run this command to show help message.
Note : we don’t need -cli suffix here.
Step 5 — Initiating React Native Application
Use the React Native command line interface to generate a new React Native project called “AwesomeProject”, then run react-native run-android inside the newly created folder.
If everything is set up correctly, you should see your new app running in your Android device shortly.
Step 6 — Connecting Android Device to Computer
Enable Debugging over USB
Most Android devices can only install and run apps downloaded from Google Play, by default. You will need to enable USB Debugging on your device in order to install your app during development.
To enable USB debugging on your device, you will first need to enable the “Developer options” menu by going to Settings → About phone and then tapping the Build number row at the bottom seven times. You can then go back to Settings → Developer options to enable “USB debugging”.
Plug in our device via USB
Let’s now set up an Android device to run our React Native projects. Go ahead and plug in your device via USB to your development machine.
Next, check the manufacturer code by using lsusb (on mac, you must first install lsusb). lsusb should output something like this:
These lines represent the USB devices currently connected to your machine.
You want the line that represents your phone. If you’re in doubt, try unplugging your phone and running the command again:
You’ll see that after removing the phone, the line which has the phone model (“Motorola PCS” in this case) disappeared from the list. This is the line that we care about.
From the above line, you want to grab the first four digits from the device ID:
22b8:2e76
In this case, it’s 22b8. That’s the identifier for Motorola.
You’ll need to input this into your udev rules in order to get up and running:
Make sure that you replace 22b8 with the identifier you get in the above command.
Now check that your device is properly connecting to ADB, the Android Debug Bridge, by running adb devices.
Seeing device in the right column means the device is connected. You must have only one device connected at a time.
Running our app
Type the following in your command prompt to install and launch your app on the device:
If you get a “bridge configuration isn’t available” error, see Using adb reverse. Hint : You can also use the React Native CLI to generate and run a Release build (e.g. react-native run-android –configuration Release).
Connecting to the development server
You can also iterate quickly on a device by connecting to the development server running on your development machine. There are several ways of accomplishing this, depending on whether you have access to a USB cable or a Wi-Fi network.
Method 1 — Using adb reverse (recommended)
You can use this method if your device is running Android 5.0 (Lollipop), it has USB debugging enabled, and it is connected via USB to your development machine.
Run the following in a command prompt:
You can now use Reload JS from the React Native in-app Developer menu without any additional configuration.
Method 2 — Connect via Wi-Fi
You can also connect to the development server over Wi-Fi. You’ll first need to install the app on your device using a USB cable, but once that has been done you can debug wirelessly by following these instructions. You’ll need your development machine’s current IP address before proceeding.
Open a terminal and type /sbin/ifconfig to find your machine’s IP address.
Make sure your laptop and your phone are on the same Wi-Fi network.
Open your React Native app on your device.
You’ll see a red screen with an error. This is OK. The following steps will fix that.
Open the in-app Developer menu.
Go to Dev Settings → Debug server host for device.
Type in your machine’s IP address and the port of the local dev server (e.g. 10.0.1.1:8081).
Go back to the Developer menu and select Reload JS.
Step 7 — Installing React Native Application into Device
Now that we have setup all the development tools, all we need to do is to test/install our app into device. Please make sure that we have already connecting our device with computer using USB connection.
If we have problem during initiating application with command
we can manually install apk file using adb. Run this command to install our app into android device.
If we want to start developing, we have to start react server and enabling livereload from in app menu. To start react server, enter into root directory of our react project and run this command.
To enabling live reload :
open our app that has already installed
press option button and select Enable Live Reload
Last updated
Was this helpful?